The Network Layer
Overview
The link layer is responsible for sending data between two nodes which have a direct connection between each other. But it only allows us to communicate with those machines with a direct connection.
The network layer allows us to communicate with nodes that are connected any where in the network.
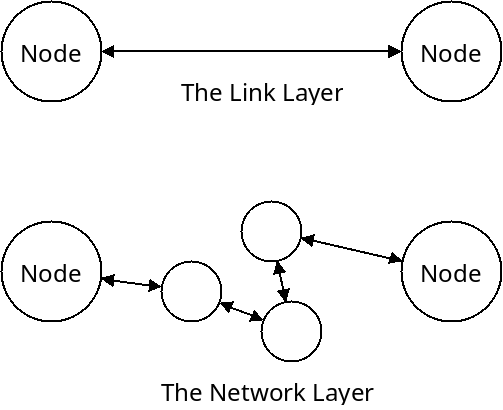
The main task of the network layer is to get packets from any one node in the network to any other node. There are two main tasks that are accomplished by the network layer:
Forwarding
Forwarding is when a single node in the network receives a packet and must decide where to send it next. This is a local decision and must be made quickly (on the nanosecond scale). Forwarding is normally done in hardware.
Routing
Routing is the global decision of how a packet should go from its source to its final destination. This is done in software and typically takes much longer (on the second or millisecond scale).
Unlike other layers, there is one predominant network layer protocol which is the "Internet Protocol", or IP.
IP Addresses
In order to perform forwarding or routing, we first need to have some way of representing a packets source and destination. IP uses addresses for this purpose. In version 4 of IP, addresses are 32-bits. In version 6 of IP, addresses are 128-bits.
IPv6 offers many more addresses than IPv4, and will need to be adopted as the Internet grows. However, IPv4 is currently still used far more widely than IPv6, so that is what we will discuss here. Differences between the two versions are small, and will be pointed out.
An IPv4 address is 32 bits, which is 4 bytes. They are typically written in dotted decimal notation. Here, each of the 4 bytes are written in decimal, with dots separating them. Each of the values can range from 0 to 255.
For instance, the IP address 132.68.99.101 is the four-bytes with those
decimal values. It can be translated into binary as 10000100 01000100
01100011 01100101.
Because there are 32 bits, there are 232 possible IP addresses which is just over 4 billion. We are just about out of these addresses, though there are ways to avoid the problem as we will see later.
IPv6 uses 128 bits for each address. This means there are 2128 possible IPv6 addresses. This is a very large number, enough to assign an address to every atom on the surface of the earth 100 times over.
Subnets
IP addresses are not just assigned randomly to different hosts and routers, instead they are generally assigned hierarchically. Usually the first $N$ bits determine which subnet a machine is a part of.
A subnet, also just called a network, is a small portion of the Internet run by one home or business. In the figure below, there are two subnets connected together. The first has three machines with addresses beginning with the "210.1.1" prefix.
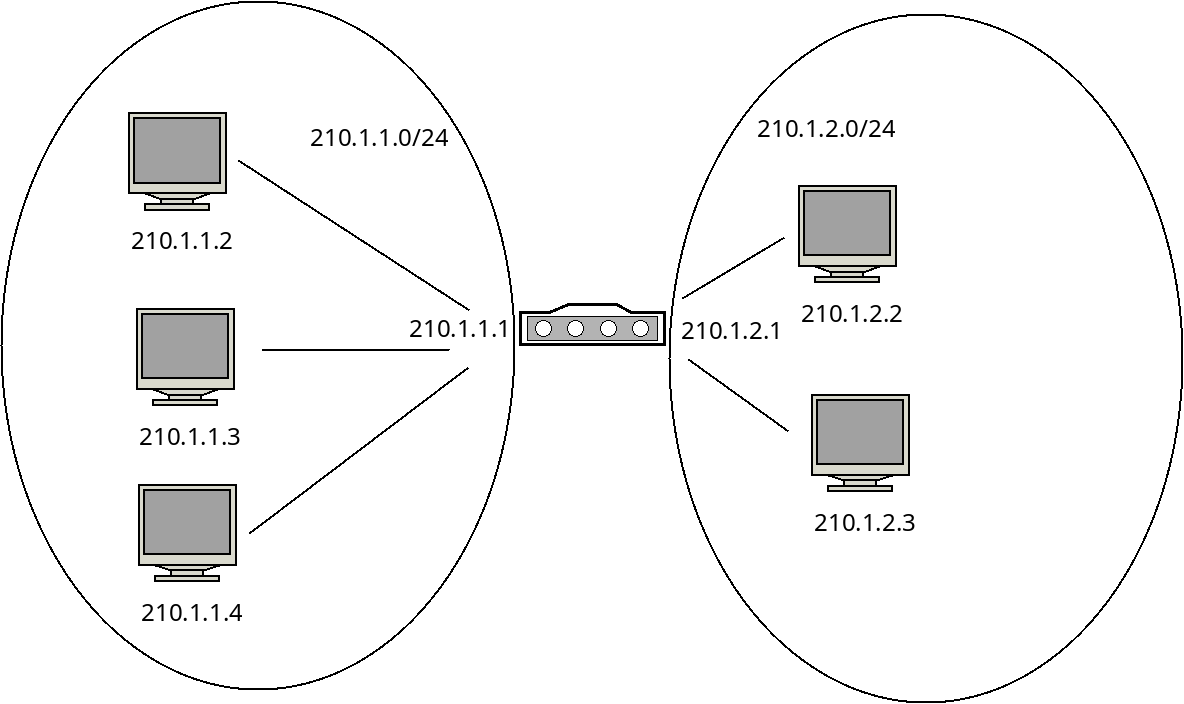
Machines in the second subnet all start with "210.1.2". In this way the first three bytes (24 bits) tell us which subnet a machine is part of. The last byte (8 bits) tell us which machine in that subnet we are talking about.
We will often write the address of the subnet by giving the portion of the address that identifies it, followed by a slash, and then the number of bits in the subnet address, for example "210.1.1.0/24" for the first subnet in the figure.
Sometimes, subnets are identified with a subnet mask which identifies
which bits are part of the subnet address and which identify individual machines.
If a bit is part of the subnet address, it is a 1 in the mask, otherwise it's a 0.
In the examples above, the masks would be 255.255.255.0. A byte of
all 1's is 255, so this signifies the first three bytes are all part of the subnet
address and the last is not.
Obtaining an IP Address
Originally, the Internet used a classful addressing scheme which separated the Internet of subnets of different classes:
| Class | Subnet Bytes | Number of Addresses |
|---|---|---|
| A | 1 | 16 million |
| B | 2 | 65 thousand |
| C | 3 | 256 |
In this scheme, if you needed to establish a network, you had to decide which class to create. If you needed, say, 300 machines in the network, you had to obtain a class B network. This was of course quite wasteful since many addresses were assigned to subnets that would never use them.
Now the Internet uses a classless strategy called Classless Interdomain Routing (CIDR). This allows the creation of subnets with any number of bits for the subnet address. The example network above uses 24 bits, but you could create a subnet with 10 bits, or any other value.
The Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) is in charge of assigning blocks of IP addresses. It allocates numbers to ISP companies which sell them to individual businesses and organizations.
Once a subnet has been created, the subnet portion of an address is fixed. But how do individual hosts know which particular address they have in that network? They can be assigned manually when the network is setup, but it's more common to use a protocol called DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol).
DHCP allows a host to obtain an IP address on a subnet automatically. DHCP is widely used, because most people do not wish to configure IP addresses manually, especially with devices like laptops and phones that connect to multiple networks throughout the day.
DHCP has four main steps:
- The new host sends a broadcast message to all nodes in the subnet. This is
done by sending to the special IP address
255.255.255.255which causes all nodes to forward the message on. The message is a "discover message" asking for an address When this is seen by the DHCP server (often builtin to a router), it handles the request. - The DHCP server then sends back a "offer message" which offers a particular IP address. This message also comes with a lease time which is the amount of time the IP address will be valid for, usually around a day. This message is also broadcast to all hosts on a subnet.
- When the client accepts an offer, it sends back a "request message" which repeats the fields in the offer message back tom the server.
- Finally the server sends an acknowledgement message back to the client.
DHCP also allows a client to ask for a renewal of its allocated IP address if it is still being used.
Network Address Translation
Because there are a limited number of IPv4 addresses, but many devices connected to the Internet, we have come up with a trick to give multiple devices what appears to be the same IP address. This is very widely used in subnets and is called Network Address Translation, or NAT.
For example, consider the following network with three hosts and one router:
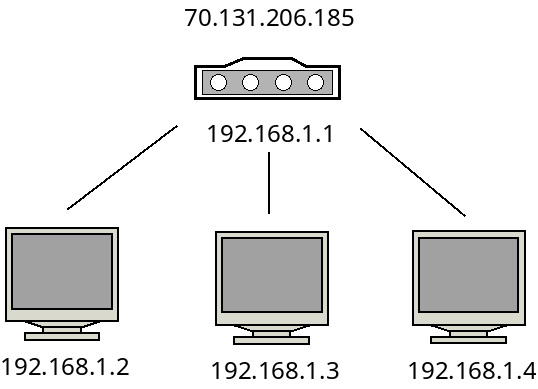
Here, the machines in the subnet are given IP addresses beginning with
192.168.1. These are local, or internal IP addresses and only
make sense inside of this subnet. The router has both an internal IP and
an external IP address.
When one of these three machines communicate with the outside world, they
will all appear to be using the address 70.131.206.185.
The following IP address ranges are reserved for these local addresses:
10.0.0.0through10.255.255.255172.16.0.0through172.31.255.255192.168.0.0through192.168.255.255
NAT makes all traffic coming out of a subnet use one "real" IP address. This greatly saves IP address space, but it gives us an issue to solve: How do foreign machines communicate with particular machines on a subnet?
For example, say that all three of the machines in the subnet request various Wikipedia articles? The Wikipedia web server sees these as all coming from the same machine. How can it give the right page to the right client?
The answer is that the router keeps track of this for us. When a packet is sent from one of the hosts through the router, the router does the following things:
- It generates a port number for the request and replaces the original port number with this new value in the packet.
- It replaces the local IP address with the external IP address in the packet.
- It stores this port/address combination in a NAT table.
For instance, when a host connects to Wikipedia, it will have the destination IP
address and port fixed. It will initially have the source IP address of 192.168.1.2
along with some source port number, let's say 10802. The router will generate a new port
number, let's say 93407 for this communication. It will then doctor up the packet so that
the source has this new port number and the external IP 70.131.206.185. It then
puts this entry into the NAT table:
| NAT Port | Source IP | Original Port |
|---|---|---|
| 93407 | 192.168.1.2 | 10802 |
The Wikipedia server then sees the port number for its client as 93407. When it sends a response,
it will include this port number. When the router gets the response, it can look back in the NAT
table and know to forward all communication with that port number to the client at 192.168.1.2.
It will also fix the packets back with the original port number for the host.
If all three machines connect to Wikipedia, the router will give them different port numbers, and so there will be different NAT table entries for them. That way the router can forward all the traffic to the right hosts. Moreover, the hosts do not need to know that their IP address is not "real".
IP Packets
Below is a diagram of an IP version 4 packet:
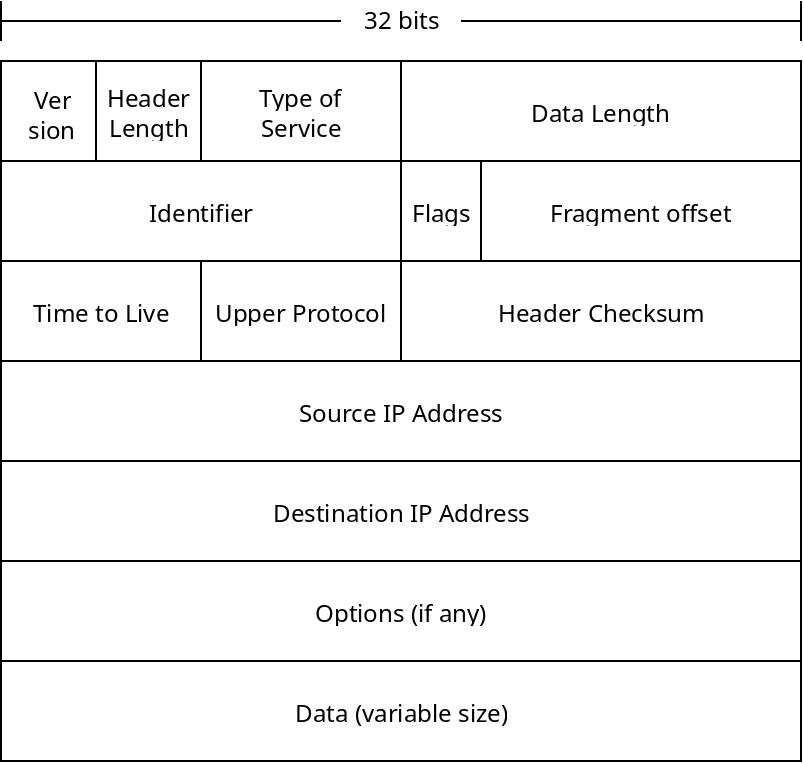
The many fields are described below:
- Which version of IP is this packet for?
- The number of bytes of the IP header. There are options which may be included, so the size can vary. Normally there are no options, and the header is 20 bytes.
- Type of service bits allow for networks to prioritize certain types of communication, for example real-time voice data might prioritized over email packets.
- The data length is how many bytes of data are included in the packet. They usually are no larger than 1500 bytes, so they can fit into an Ethernet frame.
- The identifier, flags and fragment offset deal with packet fragmentation. It is possible that an IP packet will be broken into multiple link layer frames. These fields allow the router receiving the frames to re-assemble them into 1 complete packet.
- The time to live field is to prevent packets from cycling around the network endlessly. This field is an integer which is decremented each time the packet is forwarded. If the value reaches 0, the packet will be dropped instead of forwarded further. The initial value is often 64.
- The upper layer protocol field distinguishes what sort of data is contained, this is principally TCP or UDP.
- The header checksum contains a checksum on the header information, so the data can be verified by the receiver.
- The source and destination IP addresses are the initial source node and final destination node of the packet.
- Options are not normally included, they include things like specifying routing parameters, and experimental routing options. Many routers block these even if they are included.
- Finally the data is the TCP or UDP packet that the IP layer is meant to be sending.
IPv6 packets are extremely similar with the following differences:
- There are no identifier, flags or fragment offset fields. IPv6 does not allow packets to be fragmented.
- There is no options field.
- The source and destination IP addresses are 128 bits instead of 32.
Routers
Now that we have discussed the way hosts are addressed, and what comprises IP packets, we can look at how they are forwarded through the network. A diagram of a router is given below:
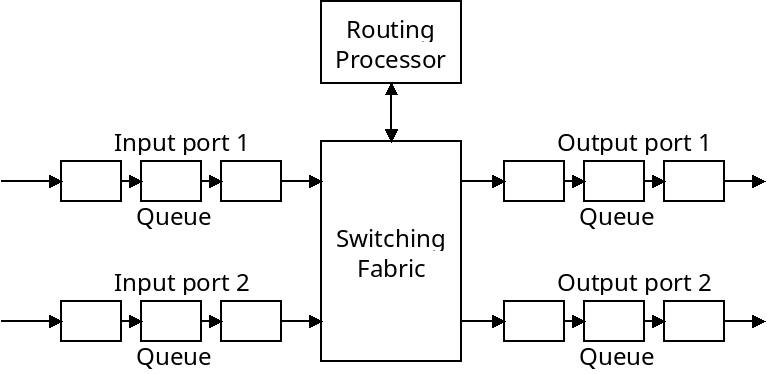
The main job of the router is to take in packets from one or more input ports, and pass them along to one of its output ports. Packets may be stored in queues as they are waiting to be forwarded.
The "switching fabric" connects the input ports with the output ports. This could be done with a shared bus, which means only one transmission can happen at a time. It could also be done with a crossbar network which means multiple transmissions could happen at the same time.
These two approaches are depicted below:
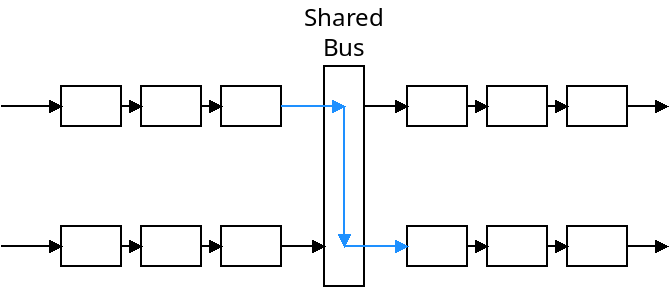
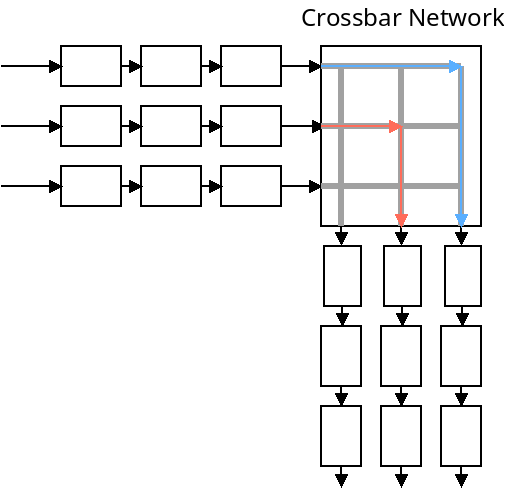
A shared bus is usually sufficient for small, home and office routers. Crossbar networks are more efficient, however.
Queueing
A router's queues are small memory locations that can hold packets as they are waiting to be processed. As depicted, packets can be stored in queues before or after being forwarded. The reason input queues are needed is because the router may receive packets faster than it can forward them. It needs output queues because it may forward packets faster than they can be sent out.
What happens if a queue becomes full? The router simply drops the packets which come after that point. IP makes no guarantees to deliver anything, it just does the best it can.
There are many, many ways that the queues can operate. Three common approaches are:
- As First in, first out (FIFO). In this scheme, packets simply wait in line, in the order they come in, to be forwarded. What are the downsides of this approach?
- As a priority queue. In this scheme, some packets are prioritized and are forwarded before others. In the simplest setup, there is one queue for each priority level. Packets in the highest priority queue are forwarded first. Only when it's empty do lower priority packets get forwarded. What are the downsides to this?
- Using weighted fair queueing (WFQ). In this scheme, we still have multiple queues for each priority level. However, we don't just stay on the highest priority queue until it's empty. Instead, we spend some amount of time on each of them. For instance we might have three priority levels. The highest could be given 60% of the router's time, the middle could be given 30%, and the lowest 10%. The router will then switch between the three queues, splitting its time based on the weights.
WFQ is widely implemented, but there are many more queueing strategies.
Forwarding
So once a router picks a packet to forward, how does it actually determine where to send it? It decides based on the packet's IP address. Routers maintain tables that tell it which of its output interfaces to put a packet on based on where its IP address falls. Because IP addresses are hierarchical, it does this based on the prefix of the address. For instance, we might have the following:
| Prefix | Output Interface |
|---|---|
| 10.1 | 1 |
| 10.2 | 2 |
| 10.3 | 3 |
| 10.3.99 | 4 |
| Otherwise | 5 |
Here we have a possible routing table for a router that could be part of an organization's network. The first three entries tell the router to forward packets with those particular prefixes to other routers.
The fourth looks like it may present a problem. It overlaps a portion of the third rule. In this case, routers will always pick the longest prefix that matches. This way, addresses starting with 10.3.99 will go to one particular link, while others starting with 10.3 will go someplace else.
The "otherwise" rule tells the router to send all other packets to another interface by default (probably to the ISP as they aren't part of this subnet).
Routers perform hardware lookups on these tables to quickly forward packets throughout the network.
Conclusion
We have covered the complex topic of how different nodes in the global Internet can be addressed, what is inside of IP packets, and how routers operate.
We've seen that routers use routing tables to forward packets. The next obvious question is, how do these routing tables get built in the first place? Also, if the network changes, how do they get updated?
The answer to these questions lie in routing algorithms which we will cover next time.